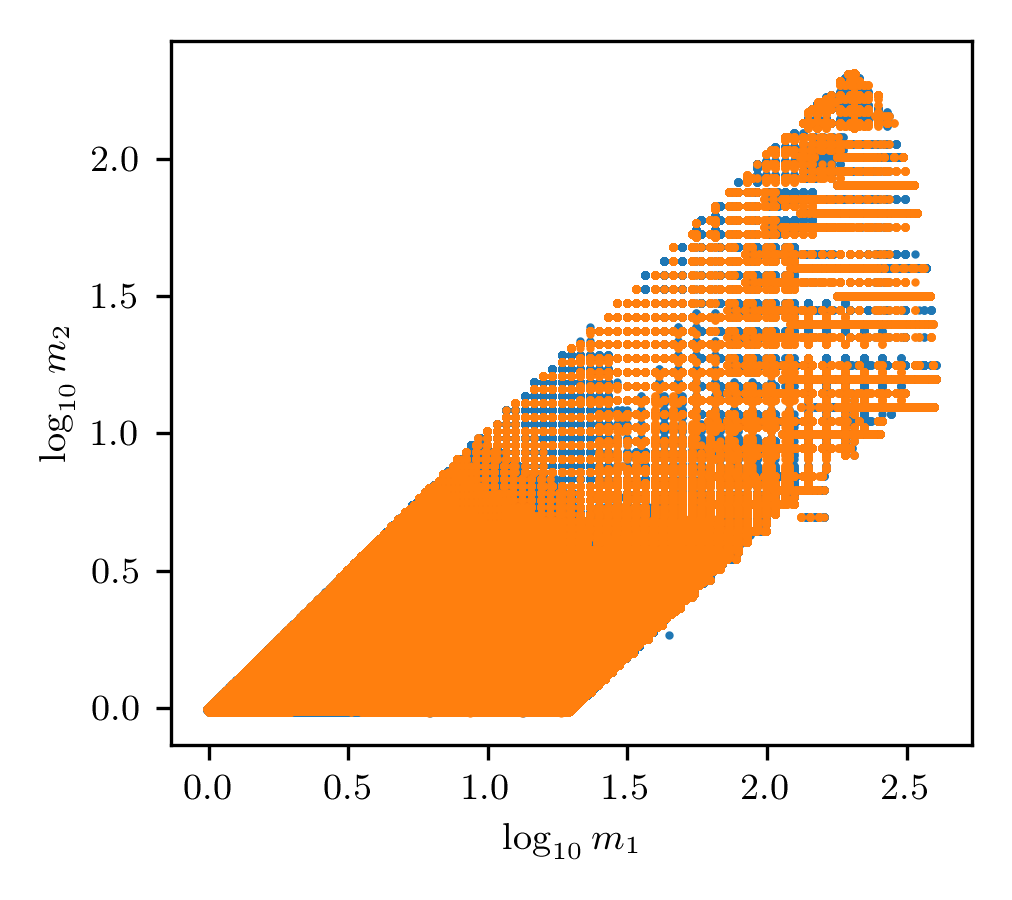
This analysis targets core compact binary systems with LIGO and Virgo. The component masses range from 1 to 200 solar masses. Components above 3 solar masses have spin ranging from -0.99 to +0.99. Components below have spins ranging from -0.05 to +0.05.
GraceDB Gitlab EpicThe following instances are associated with this analysis:
- cluster -
ssh gstlalcbc.online@submit.ligo.uwm.edu - container -
docker://containers.ligo.org/gstlal/o4b-containers:bob - run path -
/home/gstlalcbc.online/observing/4/c/runs/trigs.bob_o4c - build path -
/home/gstlalcbc.online/observing/4/c/builds/gstlal_bob_o4c_cc259c1d.sif
- cluster -
ssh gstlalcbc@ligo-hd-01.gwave.ics.psu.edu - container -
docker://containers.ligo.org/gstlal/o4b-containers:rick - run path -
/ligo/home/ligo.org/gstlalcbc/observing/4/c/runs/trigs.rick_o4c - build path -
/ligo/home/ligo.org/gstlalcbc/observing/4/c/builds/gstlal_rick_o4c_9aa5c3b8.sif
- cluster -
ssh gstlalcbc@ligo01.gwave.ics.psu.edu - container -
docker://containers.ligo.org/gstlal/o4b-containers:esme - run path -
/ligo/home/ligo.org/gstlalcbc/observing/4/c/runs/trigs.esme_o4c - build path -
/ligo/home/ligo.org/gstlalcbc/observing/4/c/builds/gstlal_esme_o4c.sif
References:
Tsukada et al Improved ranking statistics of the GstLAL inspiral search for compact binary coalescences (2023) : Description of several new improvements to the ranking statistics of the GstLAL inspiral pipeline.Ewing et al Performance of the low-latency GstLAL inspiral search towards LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA's fourth observing run (2024) : Description of the GstLAL inspiral low-latency pipeline configuration ahead of O4 and a characterization of the pipeline's performance using the mock data challenge.
Sakon et al Template bank for compact binary mergers in the fourth observing run of Advanced LIGO, Advanced Virgo, and KAGRA (2024) : This paper describes the specific template bank used for this analysis including performance tests and coverage outside of the target parameter space.
Messick et al Analysis Framework for the Prompt Discovery of Compact Binary Mergers in Gravitational-wave Data (2017) : This paper describes more broadly the analysis methods used. It is a bit out of date, but still serves as a good starting point.
This analysis targets core compact binary systems with LIGO and Virgo. The component masses range from 1 to 200 solar masses. Components above 3 solar masses have spin ranging from -0.99 to +0.99. Components below have spins ranging from -0.05 to +0.05.
GraceDB Gitlab EpicThe following instances are associated with this analysis:
- cluster -
ssh gstlalcbc.online@gstlal.ligo.caltech.edu - container -
docker://containers.ligo.org/gstlal/o4b-containers:edward - run path -
/home/gstlalcbc.online/observing/4/b/runs/trigs.edward_o4b - build path -
/home/gstlalcbc.online/observing/4/b/builds/
- cluster -
ssh gstlalcbc@ligo-hd-01.gwave.ics.psu.edu - container -
docker://containers.ligo.org/gstlal/o4b-containers:jacob - run path -
/ligo/home/ligo.org/gstlalcbc/observing/4/b/runs/trigs.jacob_o4b - build path -
/ligo/home/ligo.org/gstlalcbc/observing/4/b/builds/

References:
Tsukada et al Improved ranking statistics of the GstLAL inspiral search for compact binary coalescences (2023) : Description of several new improvements to the ranking statistics of the GstLAL inspiral pipeline.Ewing et al Performance of the low-latency GstLAL inspiral search towards LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA's fourth observing run (2024) : Description of the GstLAL inspiral low-latency pipeline configuration ahead of O4 and a characterization of the pipeline's performance using the mock data challenge.
Sakon et al Template bank for compact binary mergers in the fourth observing run of Advanced LIGO, Advanced Virgo, and KAGRA (2024) : This paper describes the specific template bank used for this analysis including performance tests and coverage outside of the target parameter space.
Messick et al Analysis Framework for the Prompt Discovery of Compact Binary Mergers in Gravitational-wave Data (2017) : This paper describes more broadly the analysis methods used. It is a bit out of date, but still serves as a good starting point.
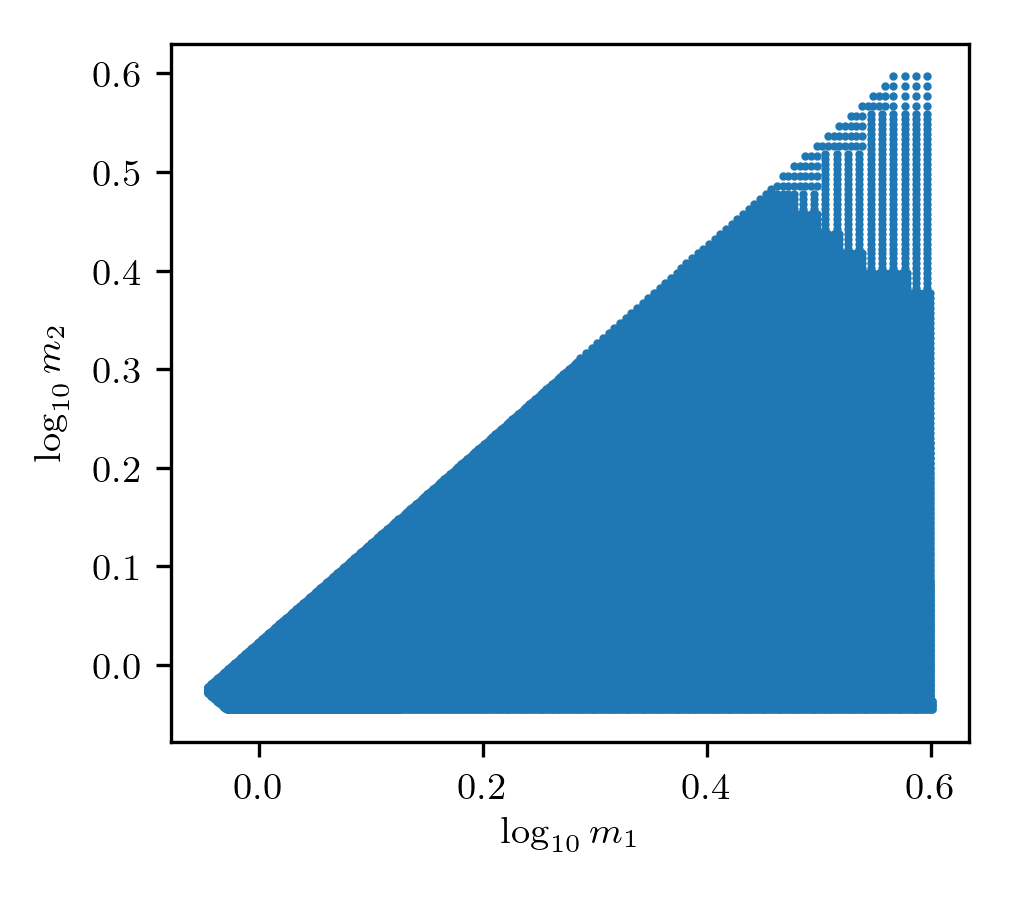
This analysis targets core compact binary neutron star and neutron star black hole systems with LIGO and Virgo. The component masses range from 0.9 to 3.9 solar masses. Spins range from -0.025 to +0.025.
GraceDB Gitlab EpicThe following instances are associated with this analysis:
- cluster -
ssh gstlalcbc.online@gstlal.ligo.caltech.edu - container -
docker://containers.ligo.org/gstlal/o4b-containers:early-warning - run path -
/home/gstlalcbc.online/observing/4/c/runs/trigs.alice_o4c - build path -
/home/gstlalcbc.online/observing/4/c/builds/gstlal_alice_o4c_0f5af171.sif
References:
Sachdev et al An early warning system for electromagnetic follow-up of gravitational-wave events (2020) : The paper describes the design and testing of an early warning gravitational-wave detection pipeline and reports sky localization bounds for detectable BNS systems.Magee et al First demonstration of early warning gravitational wave alerts (2021) : The paper presents results from an end-to-end mock data challenge that detects binary neutron star mergers and alerts partner facilities before merger. We set expectations for these alerts in future observing runs.
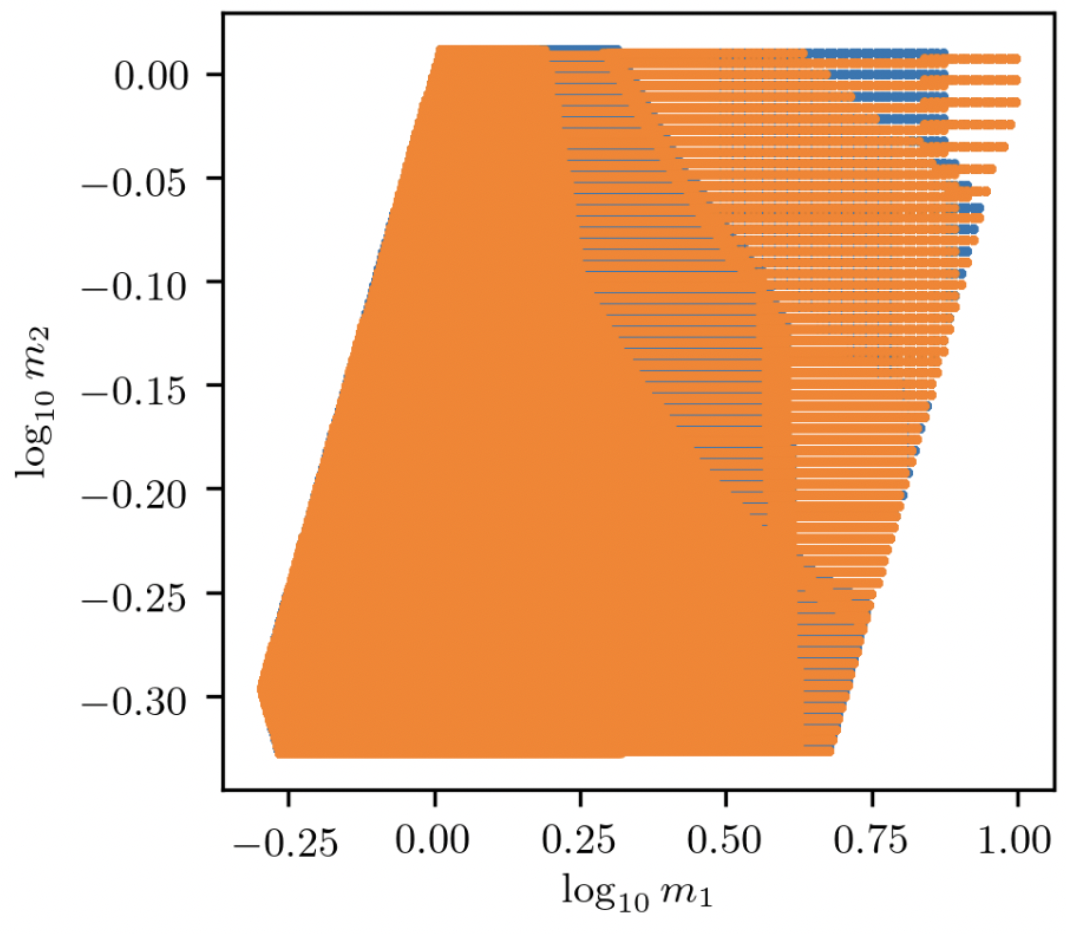
This analysis targets binary black hole systems with LIGO and Virgo. The larger component mass ranges from 0.5 to 10 solar masses while the smaller component mass ranges from 0.5 to 1 solar mass. This ensures that each binary searched for has at least one sub-solar mass component. Spin magnitudes are limited to a maximum of 0.3 . Offline searches of SSM will use a broader bank that extends down to 0.2 solar masses and spin magnitudes of 0.9 .
GraceDB Gitlab EpicThe following instances are associated with this analysis:
- cluster -
ssh gstlalcbc.online@gstlal.ligo.caltech.edu - container -
docker://containers.ligo.org/gstlal/o4b-containers:charlie-cit - run path -
/home/gstlalcbc.online/observing/4/c/runs/trigs.charlie-cit_o4c - build path -
/home/gstlalcbc.online/observing/4/c/builds/gstlal_charlie-cit_o4cb_27dd82f2
- cluster -
ssh gstlalcbc@ligo-hd-01.gwave.ics.psu.edu - container -
docker://containers.ligo.org/gstlal/o4b-containers:charlie-cit - run path -
/ligo/home/ligo.org/gstlalcbc/observing/4/c/runs/trigs.charlie-icds_o4c - build path -
/ligo/home/ligo.org/gstlalcbc/observing/4/c/builds/gstlal_charlie_o4cb_c3cc5475
References:
LIGO Scientific Collaboration, the Virgo Collaboration, the KAGRA Collaboration Search for subsolar-mass binaries in the first half of Advanced LIGO and Virgo's third observing run (2021) : This paper describes the LVK's offline search for sub-solar mass binaries in O3a. Upper limits on the merger rates of these binaries are given and used to constrain models of formation channels.LIGO Scientific Collaboration, the Virgo Collaboration, the KAGRA Collaboration Search for subsolar-mass black hole binaries in the second part of Advanced LIGO's and Advanced Virgo's third observing run (2022) : This paper describes the LVK's offline search for sub-solar mass binaries in O3b. Upper limits on the merger rates of these binaries are given and used to constrain models of formation channels.
This is a test bed for SCCB changes. Use Edward and Jacob O4b data to avoid burning in. Make sure to delete data requently in this directory.
GraceDB Gitlab EpicThe following instances are associated with this analysis:
- cluster -
ssh gstlalcbc.online@gstlal.ligo.caltech.edu - container -
docker://containers.ligo.org/gstlal/o4b-containers:edward - run path -
/home/gstlalcbc.online/observing/4/dev/runs/trigs.sccb_test - build path -
- cluster -
ssh gstlalcbc@ligo01.gwave.ics.psu.edu - container -
docker://containers.ligo.org/gstlal/o4b-containers:jacob - run path -
/ligo/home/ligo.org/gstlalcbc/observing/4/dev/runs/trigs.sccb_test_icds - build path -

References:
This analysis targets core compact binary systems with LIGO and Virgo. The component masses range from 1 to 200 solar masses. Components above 3 solar masses have spin ranging from -0.99 to +0.99. Components below have spins ranging from -0.05 to +0.05.
GraceDB Gitlab EpicThe following instances are associated with this analysis:
- cluster -
ssh gstlalcbc.online@submit.ligo.uwm.edu - container -
docker://containers.ligo.org/lscsoft/gstlal:o4b-online - run path -
/home/gstlalcbc.online/observing/4/b/runs/trigs.bob_o4b - build path -
/home/gstlalcbc.online/observing/4/b/builds/gstlal_bob_o4b_3235d59b
- cluster -
ssh albert.einstein@ligo-hd-01.gwave.ics.psu.edu && sudo -iu gstlalcbc - container -
docker://containers.ligo.org/lscsoft/gstlal:o4b-online - run path -
/ligo/home/ligo.org/gstlalcbc/observing/4/dev/b/runs/trigs.rick_mdc26_240102 - build path -
/ligo/home/ligo.org/gstlalcbc/observing/4/dev/b/builds/gstlal-dev_mdc26_240102

References:
Tsukada et al Improved ranking statistics of the GstLAL inspiral search for compact binary coalescences (2023) : Description of several new improvements to the ranking statistics of the GstLAL inspiral pipeline.Ewing et al Performance of the low-latency GstLAL inspiral search towards LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA's fourth observing run (2023) : Description of the GstLAL inspiral low-latency pipeline configuration ahead of O4 and a characterization of the pipeline's performance using the mock data challenge.
Sakon et al Template bank for compact binary mergers in the fourth observing run of Advanced LIGO, Advanced Virgo, and KAGRA (2023) : This paper describes the specific template bank used for this analysis including performance tests and coverage outside of the target parameter space.
Messick et al Analysis Framework for the Prompt Discovery of Compact Binary Mergers in Gravitational-wave Data (2017) : This paper describes more broadly the analysis methods used. It is a bit out of date, but still serves as a good starting point.
This analysis targets core compact binary neutron star and neutron star black hole systems with LIGO and Virgo. The component masses range from 0.9 to 3.9 solar masses. Spins range from -0.025 to +0.025.
GraceDB Gitlab EpicThe following instances are associated with this analysis:
- cluster -
ssh gstlalcbc.online@gstlal.ligo.caltech.edu - container -
docker://containers.ligo.org/lscsoft/gstlal:o4b-ew - run path -
/home/gstlalcbc.online/observing/4/dev/runs/trigs.ew_bns_replay_MDC27 - build path -
/home/gstlalcbc.online/observing/4/dev/builds/ew-dev_MDC27

References:
Sachdev et al An early warning system for electromagnetic follow-up of gravitational-wave events (2020) : The paper describes the design and testing of an early warning gravitational-wave detection pipeline and reports sky localization bounds for detectable BNS systems.Magee et al First demonstration of early warning gravitational wave alerts (2021) : The paper presents results from an end-to-end mock data challenge that detects binary neutron star mergers and alerts partner facilities before merger. We set expectations for these alerts in future observing runs.